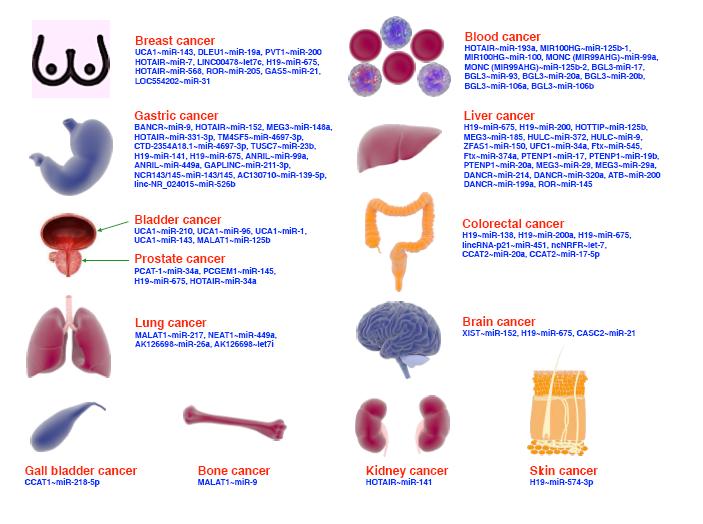
引用本文: 柳良仁,魏強(qiáng). 良性前列腺增生癥與組織炎癥. 華西醫(yī)學(xué), 2009, 24(5): 1314-1316. doi: 復(fù)制
| 1. | Berry S J, Coffey D S, Walsh P C, et alThe development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age[J]. J Urol,1984,132(3):474-479. |
| 2. | Nickel J C, Downey J, Hunter D, et al Prevalence of prostatitislike symptoms in a population based study using the National Institutes of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index. J Urol,2001,165(3):842-845. |
| 3. | Collins M M, Meigs J B, Barry M J, et al. Prevalence and correlates of prostatitis in the health professionals followup study cohort[J]. J Urol,2002,167: 1363-1366. |
| 4. | St Sauver J L, Jacobson D J, McGree M E, et al. Longitudinal association between prostatitis and development of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Urology,2008,71(3):475-479. |
| 5. | Nickel J C, Roehrborn C G, O’Leary M P, et al. The relationship between symptoms of prostatitis and histologic inflammation: Examination of baseline data from the REDUCE chemoprevention trial[J]. J Urol,2007,178(3):896-901. |
| 6. | Roehrborn C G. Definition of atrisk patients: baseline variables[J]. BJU Int,2006,97 Suppl 2:711;discussion:21-22. |
| 7. | Kramer G, Steiner G E, Handisurya A, et al. Increased expression of lymphocytederived cytokines in benign hyperplastic prostate tissue, identification of the producing cell types, and effect of differentially expressed cytokines on stromal cell proliferation[J]. Prostate,2002,52(1):43-58. |
| 8. | Steiner G E, Stix U, Handisurya A, et al. Cytokine expression pattern in benign prostatic hyperplasia infiltrating T cells and impact of lymphocytic infiltration on cytokine mRNA profile in prostatic tissue[J]. Lab Invest,2003,83(8):1131-1146. |
| 9. | Lee K L, Peehl D M. Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. J Urol,2004,172:1784-1791. |
| 10. | Kramer G, Marberger M. Could inflammation be a key component in the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia ?[J]Curr Opin Urol,2006,16(1):25-29. |
| 11. | Wang W, Bergh A, Damber J E. Chronic inflammation in benign prostate hyperplasia is associated with focal upregulation of cyclooxygenase2, Bcl2, and cell proliferation in the glandular epithelium[J]. Prostate,2004,61(1):60-72. |
| 12. | Steiner G, Kramer G, Stix U, et al. Characterization of mechanism behind the process of chronic prostatic inflammation and its role in prostatic growth[J]. Eur Urol,2004,Suppl 3(2):203. |
| 13. | Yi F X (易發(fā)現(xiàn)), Wei Q, Li H, et al Risk factors for prostatic inflammation extent and infection in benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Asian J Androl,2006,8(5):621-627. |
| 14. | Knig J E, Senge T, Allhoff E P, et al Analysis of the inflammatory network in benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer[J]. Prostate,2004,58:121-129. |
| 15. | Kramer G, Dieter M, Hrachowitz K, et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia specimens derived from patients after urinary retention show significantly more prostate glands with upregulation of HLADR and loss of CD38 than those derived from patients without urinath retention[J]. Eur Urol Suppl,2006,5(2):120. |
| 16. | Hussain T, Gupta S, Mukhtar H. Cyclooxygenase 2 and prostate carcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Lett,2003,191(2):125-135. |
| 17. | Nickel J C. The use of α1adrenoceptor antagonists in lower urinary tract symptoms: beyond benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Urology,2003,62(3 Suppl 1):34-41. |
| 18. | 王龍,王維佳,楊金瑞.良性前列腺增生合并前列腺炎的研究進(jìn)展[J].國(guó)際泌尿系統(tǒng)雜志,2006,26(2):152-155. |
| 19. | Ho C K, Nanda J, Chapman K E, et al. Oestrogen and benign prostatic hyperplasia: effects on stromal cell proliferation and local formation from androgen[J]. J Endocrinol,2008,197(3):483-491. |
| 20. | Prins G S, Korach K S. The role of estrogens and estrogen receptors in normal prostate growth and disease[J]. Steroids,2008,73(3):233-244. |
| 21. | Stone N N, Fair W R, Fishman J. Estrogen formation in human prostatic tissue from patients with and without benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Prostate,1986,9(4):311-318. |
| 22. | Smith P, Rhodes N P, Ke Y, et al. Upregulation of estrogen and androgen receptors modulate expression of FGF2 and FGF7 in human, culutured, prostatic stromal cells exposed to high concentrations of estradiol[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis,2002,5(2):105-111. |
| 23. | Untergasser G, Madersbacher S, Berger P. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: agerelated tissueremodeling[J]. Exp Gerontol,2005,40(3):121-128. |
| 24. | Di Silverio F, Bosman C, Salvatori M, et al Combination therapy with rofecoxib and finasteride in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)[J]. Eur Urol,2005,47(1):72-79. |
| 25. | Re G, Badino P, Odore R, et al Effects of mepartricin on estradiol and testosterone serum levels and on prostatic estrogen, androgen and adrenergic receptor concentrations in adult rats[J]. Pharmacol Res,2001,44(2):141-147. |
- 1. Berry S J, Coffey D S, Walsh P C, et alThe development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age[J]. J Urol,1984,132(3):474-479.
- 2. Nickel J C, Downey J, Hunter D, et al Prevalence of prostatitislike symptoms in a population based study using the National Institutes of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index. J Urol,2001,165(3):842-845.
- 3. Collins M M, Meigs J B, Barry M J, et al. Prevalence and correlates of prostatitis in the health professionals followup study cohort[J]. J Urol,2002,167: 1363-1366.
- 4. St Sauver J L, Jacobson D J, McGree M E, et al. Longitudinal association between prostatitis and development of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Urology,2008,71(3):475-479.
- 5. Nickel J C, Roehrborn C G, O’Leary M P, et al. The relationship between symptoms of prostatitis and histologic inflammation: Examination of baseline data from the REDUCE chemoprevention trial[J]. J Urol,2007,178(3):896-901.
- 6. Roehrborn C G. Definition of atrisk patients: baseline variables[J]. BJU Int,2006,97 Suppl 2:711;discussion:21-22.
- 7. Kramer G, Steiner G E, Handisurya A, et al. Increased expression of lymphocytederived cytokines in benign hyperplastic prostate tissue, identification of the producing cell types, and effect of differentially expressed cytokines on stromal cell proliferation[J]. Prostate,2002,52(1):43-58.
- 8. Steiner G E, Stix U, Handisurya A, et al. Cytokine expression pattern in benign prostatic hyperplasia infiltrating T cells and impact of lymphocytic infiltration on cytokine mRNA profile in prostatic tissue[J]. Lab Invest,2003,83(8):1131-1146.
- 9. Lee K L, Peehl D M. Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. J Urol,2004,172:1784-1791.
- 10. Kramer G, Marberger M. Could inflammation be a key component in the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia ?[J]Curr Opin Urol,2006,16(1):25-29.
- 11. Wang W, Bergh A, Damber J E. Chronic inflammation in benign prostate hyperplasia is associated with focal upregulation of cyclooxygenase2, Bcl2, and cell proliferation in the glandular epithelium[J]. Prostate,2004,61(1):60-72.
- 12. Steiner G, Kramer G, Stix U, et al. Characterization of mechanism behind the process of chronic prostatic inflammation and its role in prostatic growth[J]. Eur Urol,2004,Suppl 3(2):203.
- 13. Yi F X (易發(fā)現(xiàn)), Wei Q, Li H, et al Risk factors for prostatic inflammation extent and infection in benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Asian J Androl,2006,8(5):621-627.
- 14. Knig J E, Senge T, Allhoff E P, et al Analysis of the inflammatory network in benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer[J]. Prostate,2004,58:121-129.
- 15. Kramer G, Dieter M, Hrachowitz K, et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia specimens derived from patients after urinary retention show significantly more prostate glands with upregulation of HLADR and loss of CD38 than those derived from patients without urinath retention[J]. Eur Urol Suppl,2006,5(2):120.
- 16. Hussain T, Gupta S, Mukhtar H. Cyclooxygenase 2 and prostate carcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Lett,2003,191(2):125-135.
- 17. Nickel J C. The use of α1adrenoceptor antagonists in lower urinary tract symptoms: beyond benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Urology,2003,62(3 Suppl 1):34-41.
- 18. 王龍,王維佳,楊金瑞.良性前列腺增生合并前列腺炎的研究進(jìn)展[J].國(guó)際泌尿系統(tǒng)雜志,2006,26(2):152-155.
- 19. Ho C K, Nanda J, Chapman K E, et al. Oestrogen and benign prostatic hyperplasia: effects on stromal cell proliferation and local formation from androgen[J]. J Endocrinol,2008,197(3):483-491.
- 20. Prins G S, Korach K S. The role of estrogens and estrogen receptors in normal prostate growth and disease[J]. Steroids,2008,73(3):233-244.
- 21. Stone N N, Fair W R, Fishman J. Estrogen formation in human prostatic tissue from patients with and without benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Prostate,1986,9(4):311-318.
- 22. Smith P, Rhodes N P, Ke Y, et al. Upregulation of estrogen and androgen receptors modulate expression of FGF2 and FGF7 in human, culutured, prostatic stromal cells exposed to high concentrations of estradiol[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis,2002,5(2):105-111.
- 23. Untergasser G, Madersbacher S, Berger P. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: agerelated tissueremodeling[J]. Exp Gerontol,2005,40(3):121-128.
- 24. Di Silverio F, Bosman C, Salvatori M, et al Combination therapy with rofecoxib and finasteride in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)[J]. Eur Urol,2005,47(1):72-79.
- 25. Re G, Badino P, Odore R, et al Effects of mepartricin on estradiol and testosterone serum levels and on prostatic estrogen, androgen and adrenergic receptor concentrations in adult rats[J]. Pharmacol Res,2001,44(2):141-147.